
The Secret to Inclusive Website Design
Web design accessibility testing is critical since it has a hand in how users will interact with your website. A user-friendly site is especially crucial for users with disabilities or individuals who are not tech-savvy. Everywhere around the world, numerous users have different kinds of disabilities that limit their capability to access sites and other platforms.
Web Accessibility: The Secret to Inclusive Website Design
Inclusive website design is all about creating digital experiences that allow individuals with disabilities to interact with online interfaces. Crucial standards outline precise criteria and methods for ensuring web accessibility.
Its core principles include:
- Perceptibility;
- Operability;
- Understandability, and
- Robustness.
Websites designed with accessibility in mind can significantly impact user experience and engagement. After all, it becomes easier to use for every user, not just those with disabilities or impairments.
Accessible websites are simpler to navigate, comprehend, and interact with, leading to higher user satisfaction and engagement.
There are many important design characteristics, such as for eCommerce websites, such as usability and filter options, but accessibility is also critical.
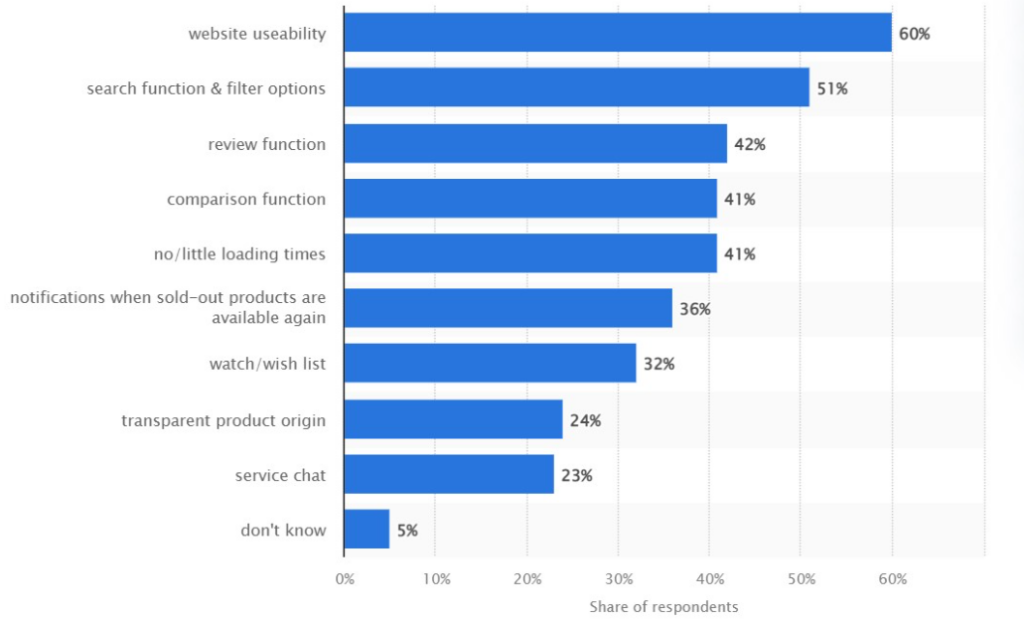
Source: Statista.
By prioritizing website design and accessibility, businesses can show their strong commitment to inclusivity.
Taking the design into consideration also helps the organization foster an equitable online environment. For instance, even the latest WordPress web design trends list accessibility compliance as an extremely crucial feature.
Conducting Accessibility Audits
In testing for accessibility, there are a number of factors you should assess to ensure a smooth interface and identify potential improvements.
Here are three recommended approaches to audit your website:
Assessing Website Accessibility with Automated Tools
Automated tools can scan or point out web pages that comply with the current accessibility standards. Furthermore, with the help of automated tools, a web Quality Assurance (QA) tester can quickly identify accessibility issues.
Some examples of these automated tools include:
WAVE Browser Extensions
This extension aids owners in evaluating web content for accessibility issues within their websites.
Accessibility Insights for Web
This Chrome extension helps developers find and fix accessibility issues in a short length of time.
Siteimprove Accessibility Checker Extension
This free extension easily checks the accessibility of any web page and identifies any issues based on the recent testing rules.
Manual Evaluation of Accessibility Features and Components
Using tools is only part of web accessibility tests; manually assessing your site can complement them. This helps in finding mistakes they may not have picked up prior.
Even after a website is launched, users may experience bugs, delays, and unresponsive features.
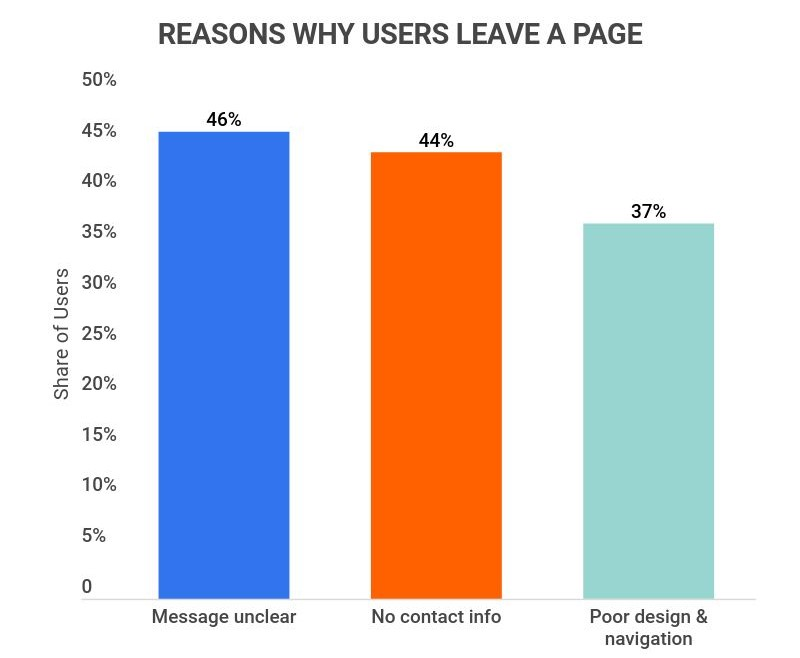
Source: Zippia.
Through manually evaluating accessibility, a Quality Assurance web tester can examine the following factors:
- Keyboard navigation,
- Screen reader compatibility, and
- Semantic HTML structure.
This approach can assist in identifying and prioritizing areas that need to be fixed or improved.
Identifying Common Accessibility Issues and Challenges
During audits, a QA tester should be able to pinpoint several common web accessibility issues and challenges. Overcoming obstacles involves using technical solutions, thoughtful design, and user testing to create an inclusive experience for people of all abilities.
Some of these issues may include:
- Alt texts that do not match on specific pages;
- Improper forms;
- Inaccessible multimedia content; and
- Complex navigation structure.
Addressing Common Accessibility Concerns
After discovering accessibility concerns via testing, QA testers can work with web developers to address them. You should address all the most common website accessibility issues first, especially if they can be resolved quickly and have happened to others prior.
Here are some helpful tips to address common accessibility issues or concerns:
Keyboard Accessibility And Navigation
The first aspect to consider is the level of interactivity your website offers through keyboard commands.
Keyboard commands are essential for basic website features such as interacting with menus, form fields, and website links. Testing website navigation using only a keyboard is crucial for an inclusive user experience.
Alternative Text For Different Multimedia Content
Alternative or alt text is the brief description of an image or media content within a specific page. These also provided further context for visually impaired users.
It’s important to provide descriptive alt text for images. These assist users with visual impairments in understanding visual website content.
HTML Markup And ARIA Attributes
Semantic HTML markup communicates content meaning and structure using tags like headings and lists. Accessible Rich Internet Applications, or ARIA attributes, define additional information for assistive technology, making web content more accessible to users.
By using both semantic HTML and ARIA attributes, website accessibility can be improved for all users, regardless of their abilities.
Testing Across Different Devices and Platforms
The next step in testing is to check whether the website is both accessible and functional through different devices. Cross-device and -platform compatibility is crucial for attracting more users to your website.
Here are the few important assessments that any QA web tester must consider:
Responsive Design Testing for Mobile Accessibility
Responsive design testing focuses on assessing the website’s designs, displays, and adaptability across different screen sizes and resolutions.
Part of the assessments includes verifying the website’s contents and whether they remain accessible and usable on every device. Having a responsive and user-friendly website ensures Quality Assurance for your business.
Compatibility Testing with Various Browsers and Assistive Technologies
Compatibility testing assesses how well the website or program performs across different browsers and devices.
Developers need to check its compatibility with popular browsers such as:
- Chrome;
- Firefox;
- Safari; and
- Edge.
They also need to ensure that the site works smoothly with screen readers, voice recognition software, and other assistive tools.
Conducting User Testing with Individuals with Disabilities
Another crucial test is to have actual users with disabilities try on the website. Observing user interactions with the interface and refining the design based on their feedback can result in a more user-friendly product.
Leveraging Automated Testing Tools and Frameworks
Automated testing tools ensure web products are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. Quality Assurance tools also scan your web page or application and find any potential issues.
A Quality Assurance web tester can utilize some of these tools, which include:
- BrowserStack;
- WebPageTest;
- Google PageSpeed Insights;
- PerfectPixel, etc.
It is crucial to prioritize accessibility throughout the development process. To achieve this, it is essential to incorporate accessibility testing into Continuous Integration (CI) pipelines.
CI pipelines automate the building, testing, and deployment of code changes, enabling teams to identify issues early and frequently.
Furthermore, regular audits can ensure ongoing accessibility compliance and spot any issues that automated tools may have missed. Manual testing can reveal concerns with keyboard navigation and screen reader compatibility.
Regular accessibility audits can help teams demonstrate their continuous commitment to inclusivity.
Educating Designers and Developers on Accessibility Best Practices
Here are some important strategies a Quality Assurance web tester can apply for smoother testing approaches.
Providing Training and Resources on Web Accessibility
Ensure you can provide up-to-date training programs and resources to your designers and developers.
Having up-to-date resources is crucial for improving website performance and ensuring that it’s accessible to all kinds of users. These resources should include the latest assistive technologies and user-friendly designs.
Incorporating Accessibility Guidelines into Design and Development Processes
It is important to use planned-out frameworks and consider them throughout the testing process. This practice involves considering frameworks like WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) throughout your website’s development process.
Encouraging a Culture of Accessibility and Inclusivity
This practice focuses on promoting empathy and understanding the value of accessibility and inclusivity in website design. Organizations can create truly inclusive digital experiences by prioritizing and championing accessibility.
Ensuring Compliance with Legal and Regulatory Requirements
Another important factor to consider is the legal obligations that come along with designing faccessibility. Organizations must ensure equal access to digital content and services for users with disabilities by complying with legal requirements.
Accessibility test requirements in contracts are crucial to ensure compliance, prevent legal issues, and promote inclusivity. It’s important to regularly monitor and make improvements as needed.
Overcoming Challenges and Adoption Considerations
Though it’s indispensable for creating top-notch web products, Quality Assurance testing comes with the following challenges:
Addressing Resource Constraints and Budget Limitations
Organizations must prioritize their strategies across resources and budget limitations. This strategy should revolve around identifying key areas that need improvements.
Integrating Accessibility into Agile and DevOps Workflows
Another consideration to keep an eye on is the accessibility of Agile and DevOps workflows.
Agile streamlines software development from concept to code completion. Meanwhile, DevOps broadens the scope to encompass delivery and ongoing maintenance.
Taking both approaches streamlines software development and results in high-quality websites.
Navigating Evolving Technologies and Accessibility Standards
Organizations must also stay informed and adaptable as technology and accessibility standards evolve. This practice involves keeping up with the latest innovative technologies and accessibility standards like WCAG.
Ongoing training for development teams can help ensure effective implementation of the latest accessibility best practices.
Future Trends and Innovations
Accessibility tests are also prone to change and adapt to the influences of growing technology.
For example, Artificial Intelligence technologies are one of the growing trends to consider. This is due to the potential for AI to automate various aspects of testing, including issue identification and solution suggestions.
It’s also recommended to integrate Voice-User Interfaces (VUIs) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) into web apps, as more people are using voice search.
Prioritizing web accessibility testing for users with disabilities is crucial. It’s a legal obligation for accessibility and promotes inclusivity. Websites and apps must cater to all users, including those with disabilities.
Conclusion
Web accessibility testing is important as it ensures your website is usable by everyone, especially people with disabilities. Accessible websites demonstrate commitment to inclusion. With these features, we mitigate user challenges to ensure a seamless experience and elevate a positive image.
Continuous effort and adaptation are necessary when it comes to designing inclusive websites. A reliable QA web tester can ensure your website’s inclusivity.
Frequently Asked Questions About Web Accessibility
What is an example of web accessibility?
One example of web accessibility is sufficient color contrast between text and backgrounds. It enables people with limited vision or color blindness to read content on a webpage.
How can I check the accessibility of a website?
You can check the accessibility of a website through automated testing tools (ex., WAVE, Axe, or Lighthouse). On the other hand, you may conduct manual tests using only a keyboard or screen reader. Important aspects to look out for include alt text on images and videos, closed captions on videos, and proper color contrast.
Does a QA tester require coding?
Coding knowledge isn’t mandatory for becoming a Quality Assurance tester, but the level of knowledge will depend on what type of tests they conduct. For example, a foundational understanding of coding is critical for automation or specialized testing.

















Comment 0